Trivia question for Oct-06-2011
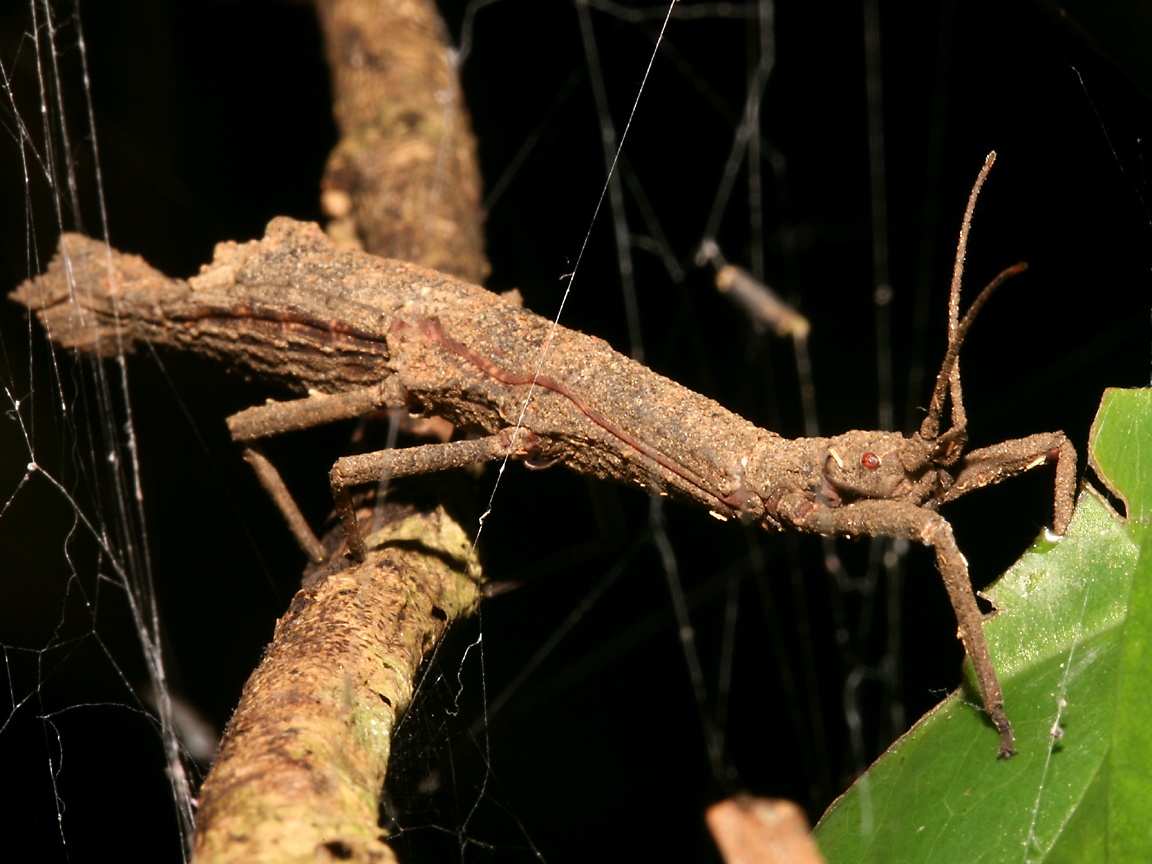

These species exhibit mechanisms for defense from predators that both prevent an attack from happening in the first place (primary defense) and are deployed after an attack has been initiated (secondary defense). Camouflage is obviously their first defense but in a seemingly opposite method of defense, many species will seek to startle the encroaching predator by flashing bright colors that are normally hidden and making a loud noise.
Trivia question for Oct-05-2011
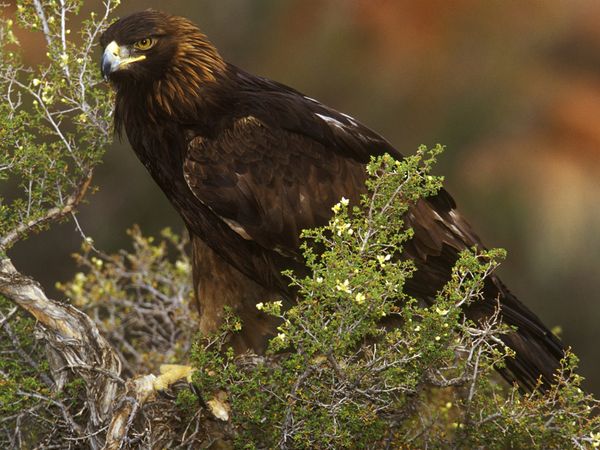

These birds have been used in falconry since the Middle Ages. In Asia, they were used in teams to hunt such animals as deer, antelope and wolves, while their use was reserved for Emperors in Europe. They can be trained for falconry.
Trivia question for Oct-04-2011
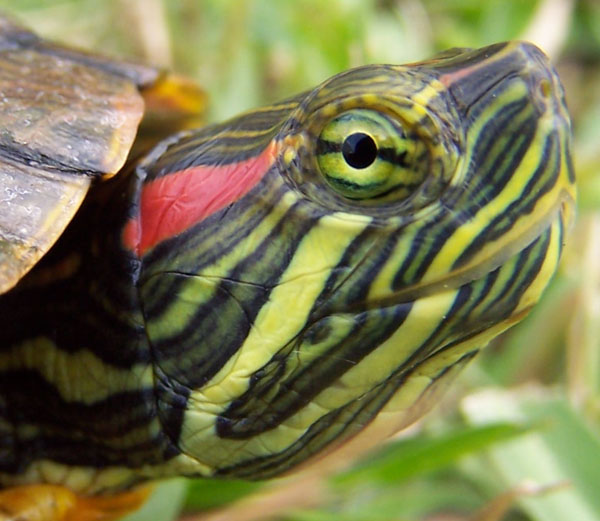

Did you know that reptiles do not hibernate, but actually brumate? This means ‘becoming less active’, but occasionally rising for food or water. Brumation can occur in varying degrees. These turtles brumate over the winter at the bottom of ponds or shallow lakes; they become inactive, generally, in October, when temperatures fall below 50 °F. Individuals usually brumate under water. They have also been found under banks and hollow stumps and rocks.
Trivia question for Oct-03-2011
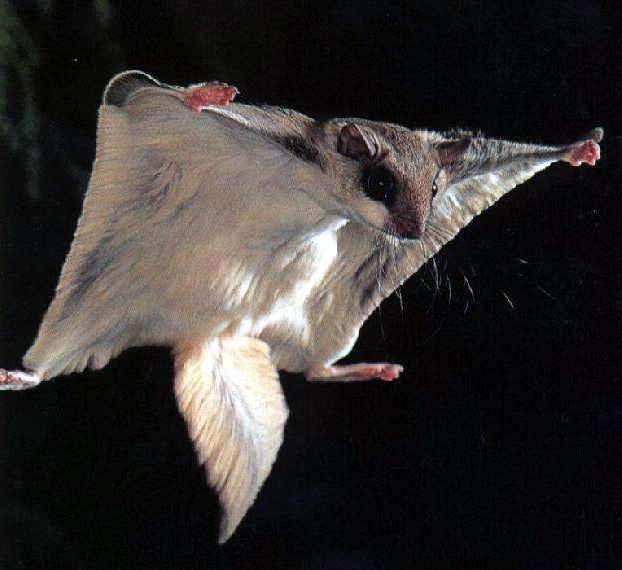

They store food, especially acorns, for winter consumption. They also dine on insects, buds, mushrooms, mycorrhizal fungi, carrion, bird eggs and nestlings and flowers. Predators include snakes, owls, hawks and raccoons. Domestic house cats can be dangerous to these animals. Although graceful in flight, they are particularly vulnerable on the ground.
Trivia question for Oct-02-2011
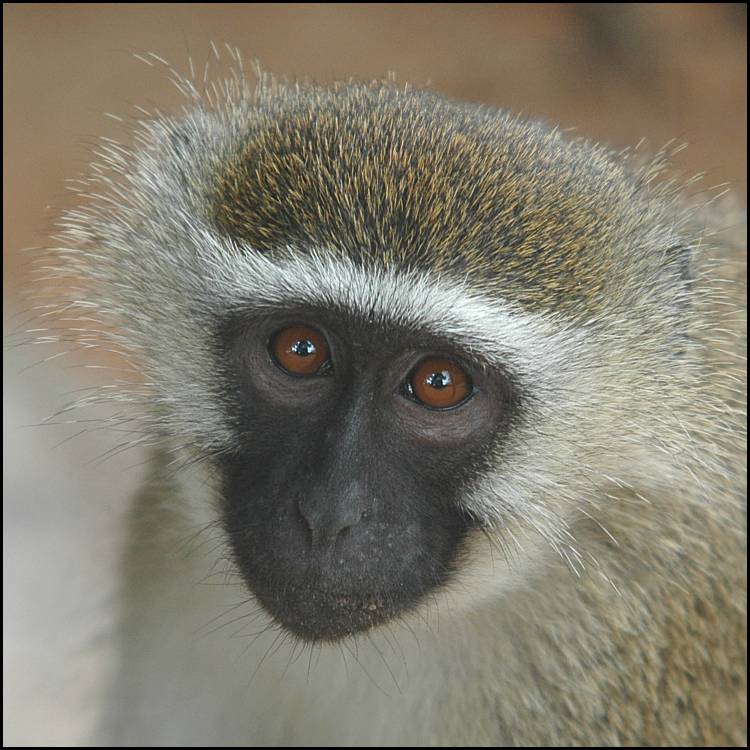

These monkey’s is diurnal and social; living in groups of up to 72. There is a clear order of dominance among individuals within the group. They eat a wide range of fruits, figs, leaves, seeds and flowers. It also eats birds’ eggs and young chicks, and insects (grasshoppers and termites).
Trivia question for Oct-01-2011
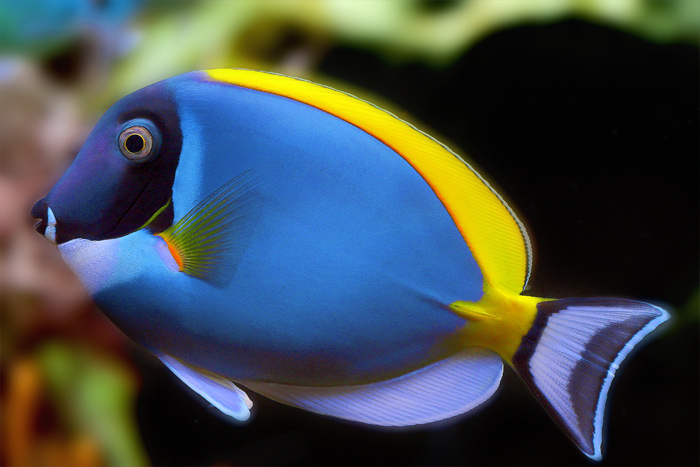

The distinctive characteristic of the family is the spines, one or more on either side of the tail, which are dangerously sharp. The dorsal, anal and caudal fins are large, extending for most of the length of the body. The small mouths have a single row of teeth used for grazing on algae.
Trivia question for Sep-30-2011
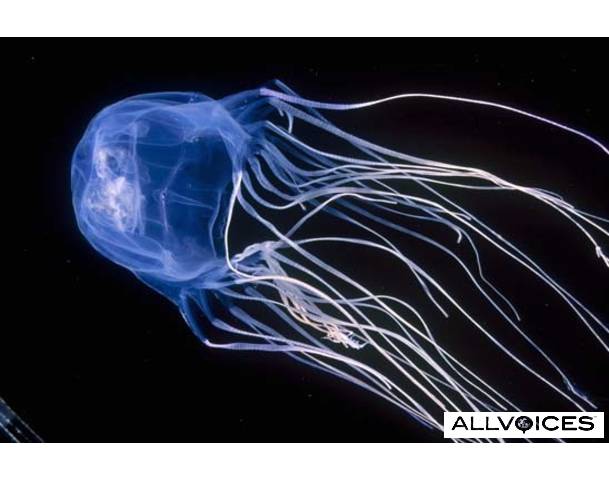
These guys trail 60 tentacles, each up to 15-feet long and armed with stinging cells. Although the notoriously dangerous species of jellies are largely, or entirely, restricted to the tropical Indo-Pacific, various species of these jellies can be found widely in tropical and subtropical oceans, including the Atlantic and east Pacific, with species as far north as California, the Mediterranean and Japan and as far south as South Africa and New Zealand.
Trivia question for Sep-29-2011
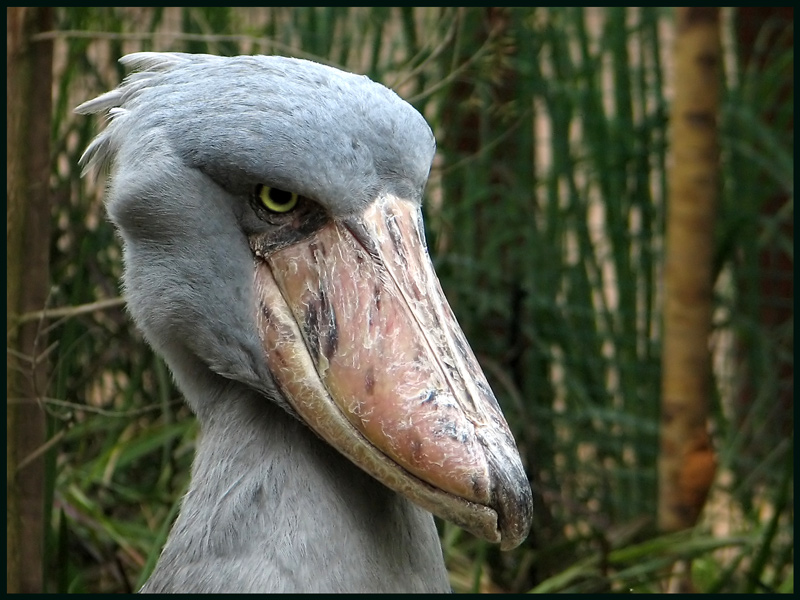

The population is estimated at between 5,000 and 8,000 individuals, the majority of which live in Sudan. Bird-Life International have classified it as Vulnerable with the main threats being habitat destruction, disturbance and hunting.
Trivia question for Sep-28-2011
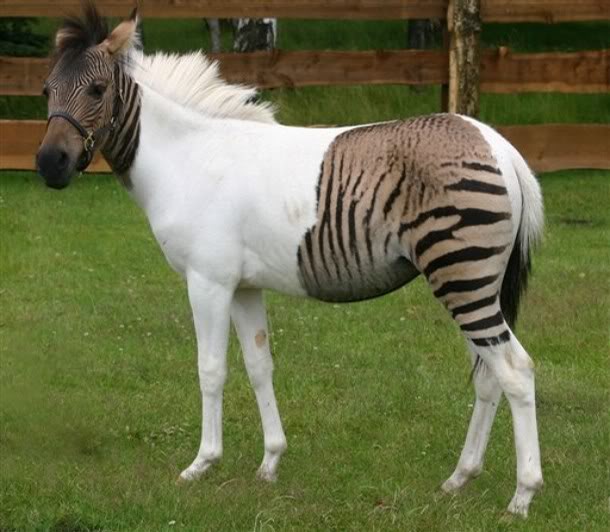

The creation of such hybrids has been going on since 1815 when Lord Morton mated a quagga stallion to a chestnut Arabian mare. The result was a female hybrid which resembled both parents. This prompted other to do their own experimenting which has resulted in these strikingly different equine.
Trivia question for Sep-27-2011
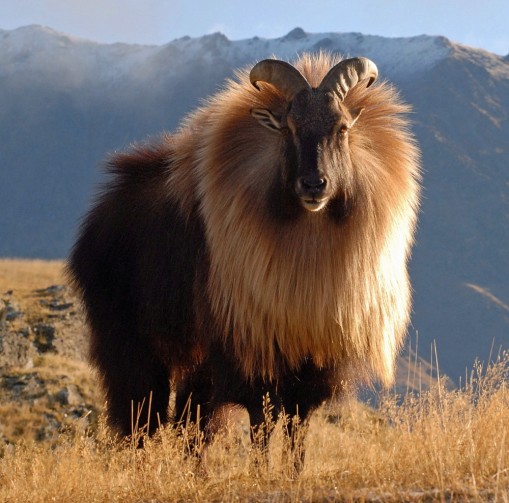

They have small heads with large eyes and small pointed ears and red circles on their cheeks. Their hooves have a flexible, rubbery core that allows them to grip smooth rocks, while a hard, sharp rim can lodge into small footholds.
Trivia question for Sep-26-2011
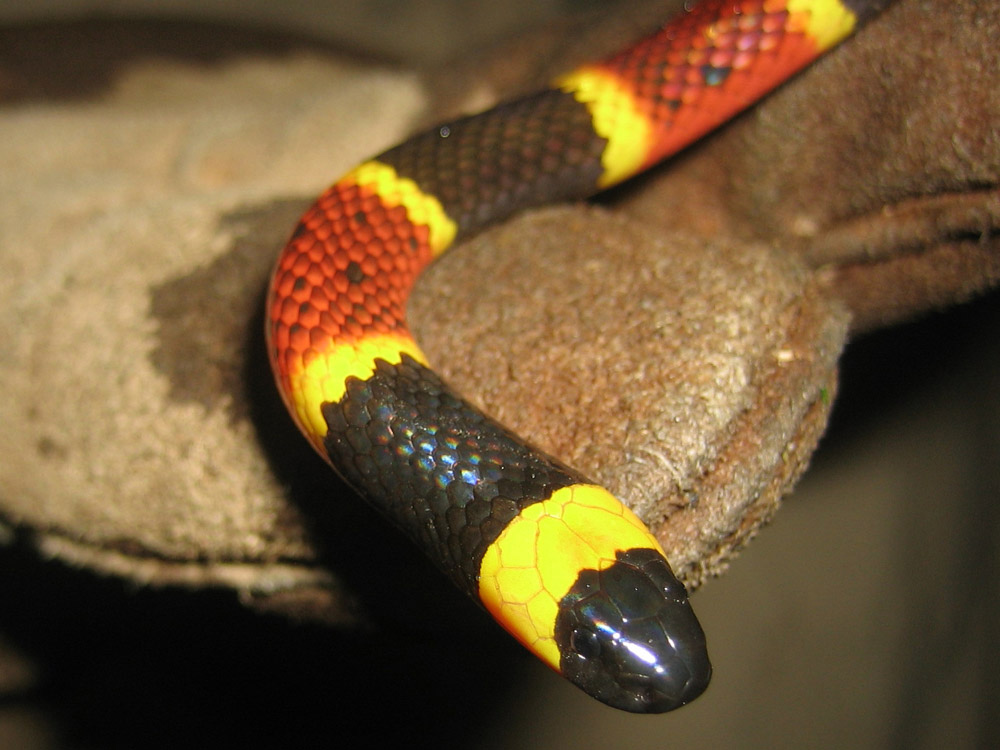

These snakes use a pair of small fangs fixed in the front of their top jaw to deliver their venom. They feed on smaller snakes, lizards, frogs, and nestling birds and rodents etc. The venom takes time to fully take effect.
Trivia question for Sep-25-2011
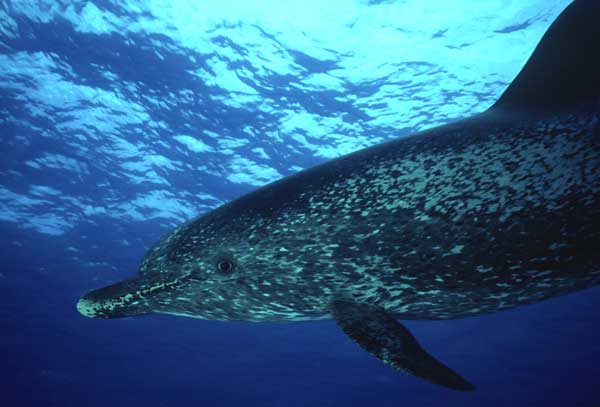

This Dolphin’s propensity for associating with Yellowfin Tuna, particularly in the eastern Pacific has in recent history been a very real danger. In the 1960s and 1970s fishermen would capture thousands of dolphin and tuna at once using purse seine nets. The dolphins all died. Over a period of about 25 years 75% of this region’s population, and over half the world’s total was wiped out.
Trivia question for Sep-24-2011
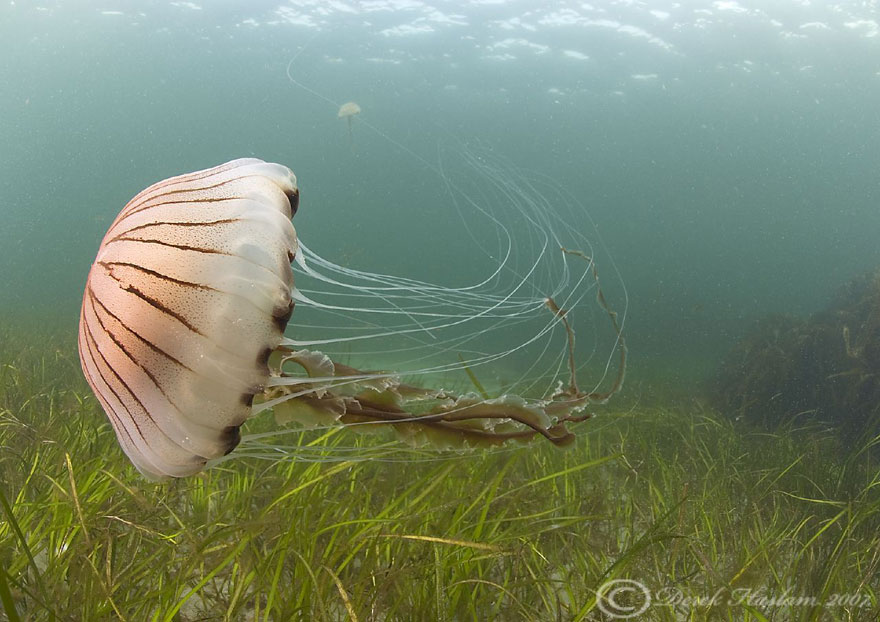

They are found in all temperate and tropical seas around the world. They feed on small planktonic animals, such as arrow-worms, comb jellies, and young polychaetes. The prey is passed to their mouths by the marginal tentacles and mouth arms.
Trivia question for Sep-23-2011
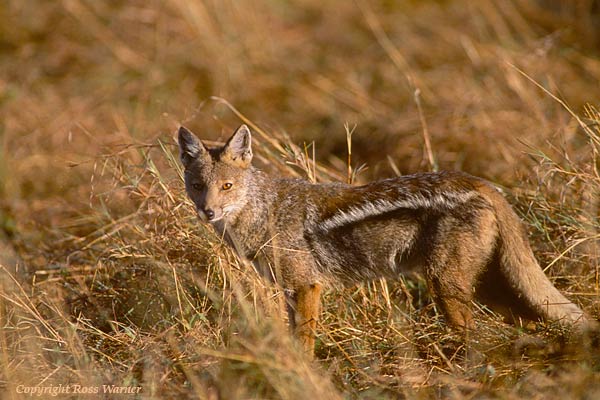

These guys tend to be less carnivorous than others of their species, and is a highly adaptable omnivore whose dietary preferences change in accordance to seasonal and local variation.
Trivia question for Sep-22-2011
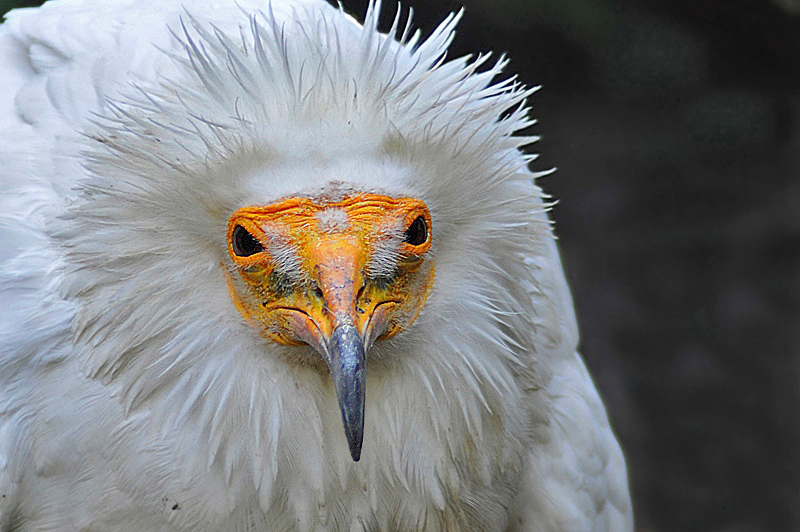

This species is often seen soaring in thermals often with other scavengers. They feed on a range of food including mammal feces (especially human), insects in dung, carrion as well as vegetable matter and sometimes small live prey. Studies suggest that feeding on mammalian (in this case, ungulate) feces helps in obtaining carotenoid pigments responsible for the bright yellow and orange facial skin.

